Connect With Us
Blogs
Displaying items by tag: alcoholism
Wednesday, 26 April 2017 12:41
Facts about Alcoholic Neuropathy
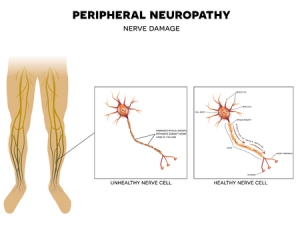
Neuropathy refers to nerve damage. One source of neuropathy in the feet is alcoholism. It’s important for patients to be forthcoming with the foot doctor about alcohol intake. In honor of National Alcohol Awareness Month we at Superior Foot & Ankle Care Center would like to offer the following facts about alcoholic neuropathy:
- The ethanol found in alcohol damages nerve tissue.
- In addition, poor diet and lack of certain vitamins (also common in alcoholics) can contribute to nerve damage.
- Symptoms of alcoholic neuropathy include: loss of sensation and numbness, tingling, pain, burning, muscle spasms and muscle weakness.
- Nerve damage caused by overuse of alcohol is usually permanent.
- There are other possible causes of neuropathy that our podiatrists, Dr. Victoria Foley and Dr. Constance Omelas will need to rule out. They will start by examining your feet and may order blood or other tests such as nerve conduction and nerve biopsy.
- Potential dangers of alcoholic neuropathy include greater likelihood of injury due to lack of sensation. Similarly, conditions such as athlete’s foot can progress to the point of open sores because the patient does not perceive the symptoms in their earlier stages. Infections are more likely to develop in these scenarios. Muscle dysfunction can increase the chance of falls.
- There are treatment options available to lessen the symptoms of alcoholic neuropathy such as B vitamins, prescription medications for pain, galvanic stimulation, magnetic therapy and orthotic inserts.
- To prevent further nerve damage from occurring, patients with alcoholic neuropathy must stop drinking. If you want information on treatment for alcoholism you can ask the foot doctor for a referral or visit ncadd.org.
If you have noticed signs of neuropathy in your feet or have other questions about this condition contact our Long Beach office to schedule an appointment by calling: 562-420-9800.
Published in Foot Health
Tagged under